Some materials about Zen3, AMD EPYC 7763 and 7773x
Updated: Oct 25th, 2023
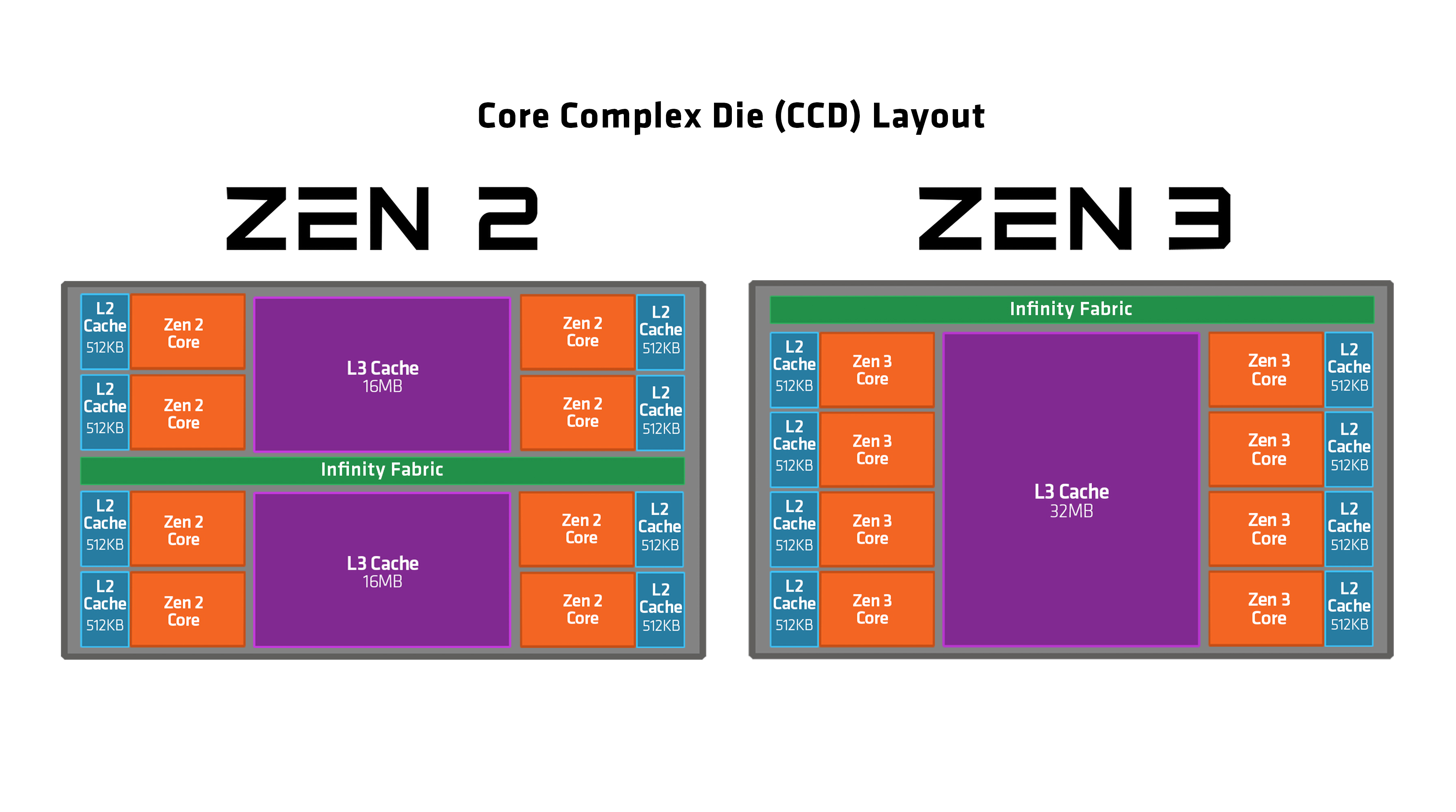
CCD in Zen3 CPU
(source)
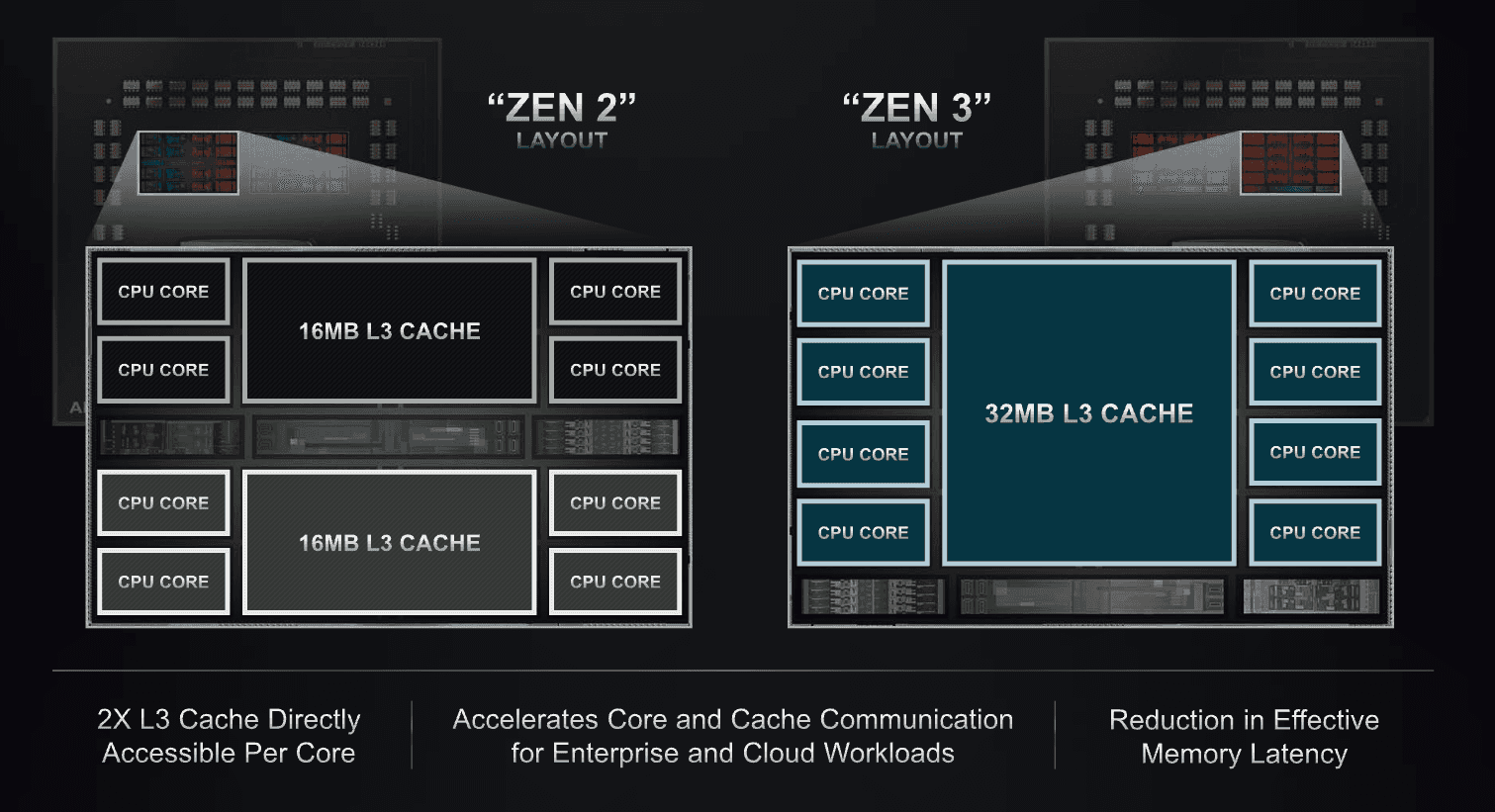
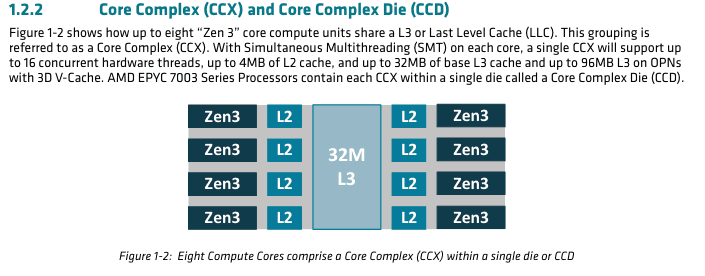
Like Zen 2, Zen 3 is composed of up to 2 core complex dies (CCD) along with a separate IO die containing the I/O components. A Zen 3 CCD is composed of a single core complex (CCX) containing 8 CPU cores and 32 MB of shared L3 cache, this is in contrast to Zen 2 where each CCD is composed of 2 CCX, each containing 4 cores each as well as 16 MB of L3 cache. The new configuration allows all 8 cores of the CCX to directly communicate with each other and the L3 Cache instead of having to use the IO die through the Infinity Fabric. ref
Zen 3 - Microarchitectures - AMD - WikiChip
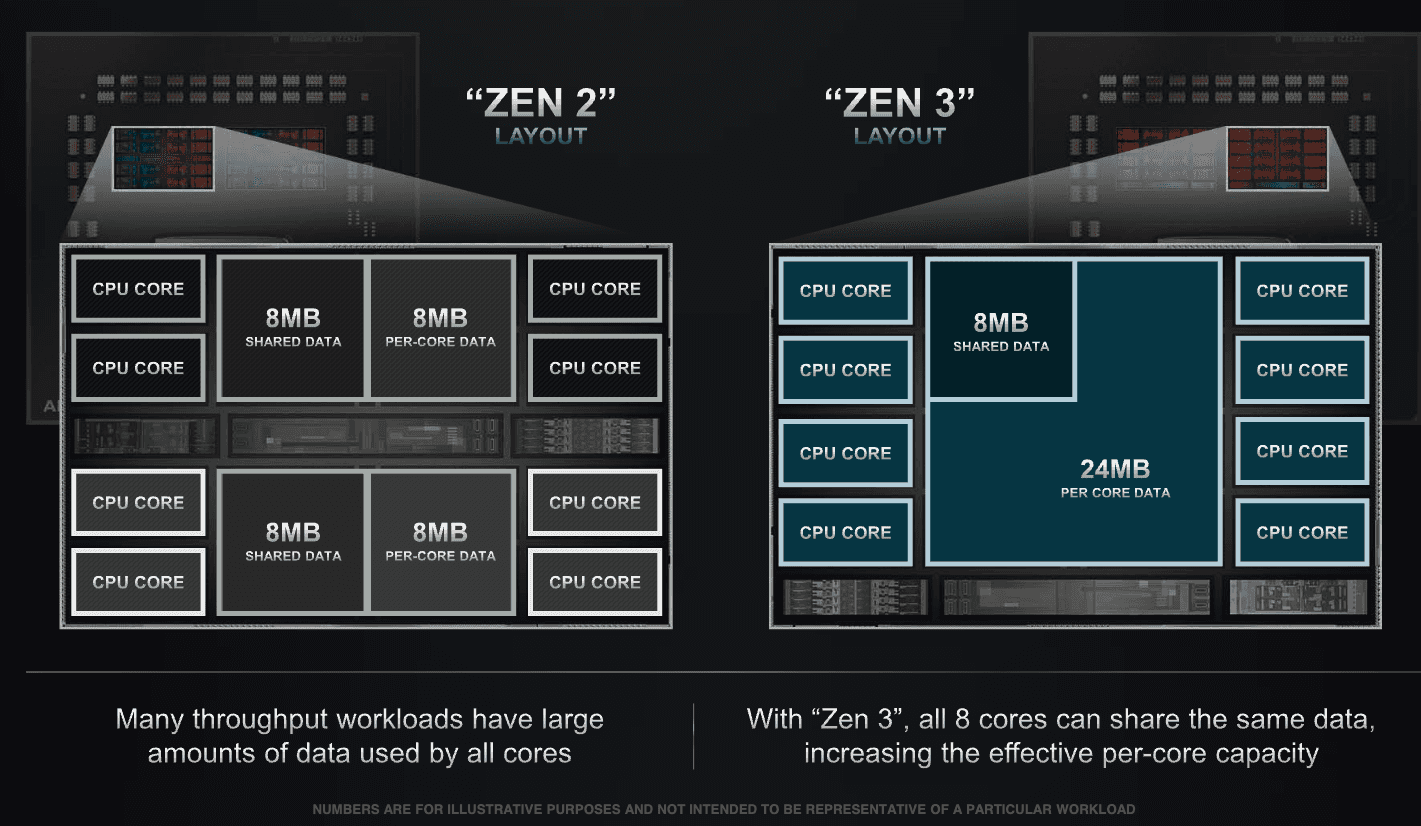
This slide indicates that the 32MB L3 cache in the CCD can be accessed by all 8 cores. Therefore, if we need to share 8MB of data among these cores, we only need to utilize 8MB of space in the L3 cache in Zen 3 CCD. The remaining 24MB can then be allocated for per-core data caching. In contrast, the Zen 2 layout requires each CCX to have its own dedicated 8MB data storage, resulting in a reduced capacity of only 16MB for per-core data caching.
Digital Launch of 3rd Gen AMD EPYC™ Processors :: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD)
Cache
for each CCD in 7763
L1i: 32 KiB per core
L1d: 16 KiB per core
L2: 512 KiB per core
L3: 32MB per CCD
Zen 3 - Microarchitectures - AMD - WikiChip
AMD EPYC 7763 Specs | TechPowerUp CPU Database
Architecture view
A long look at AMD’s Zen 3 core and chips - SemiAccurate
EPYC 7763
 (source)
(source)
The package view of 7763 is above. It have one big I/O die and 8 CCDs around it.
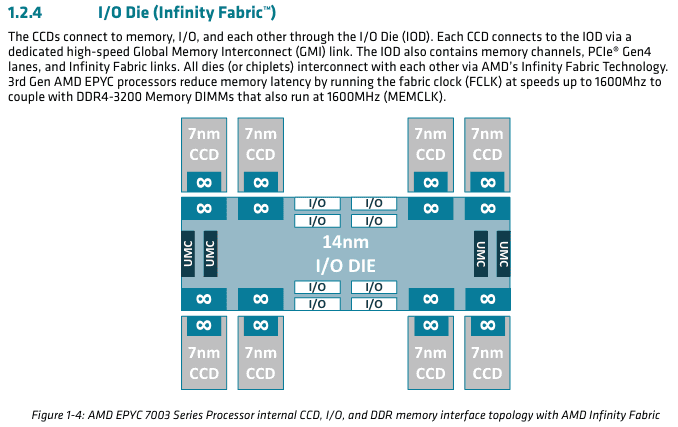 (source)
(source)
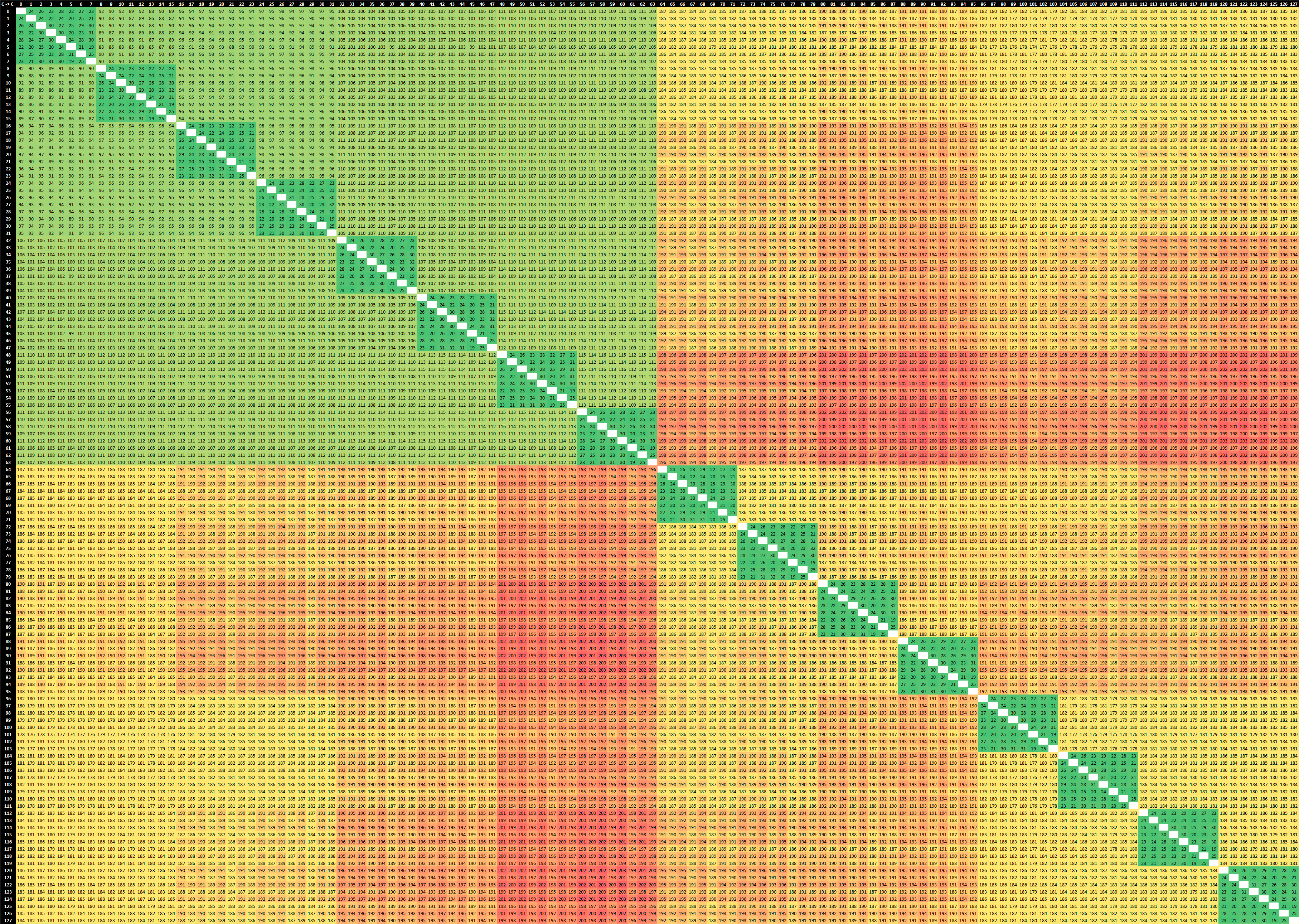
core to core latency
Memory Subsystem Topology
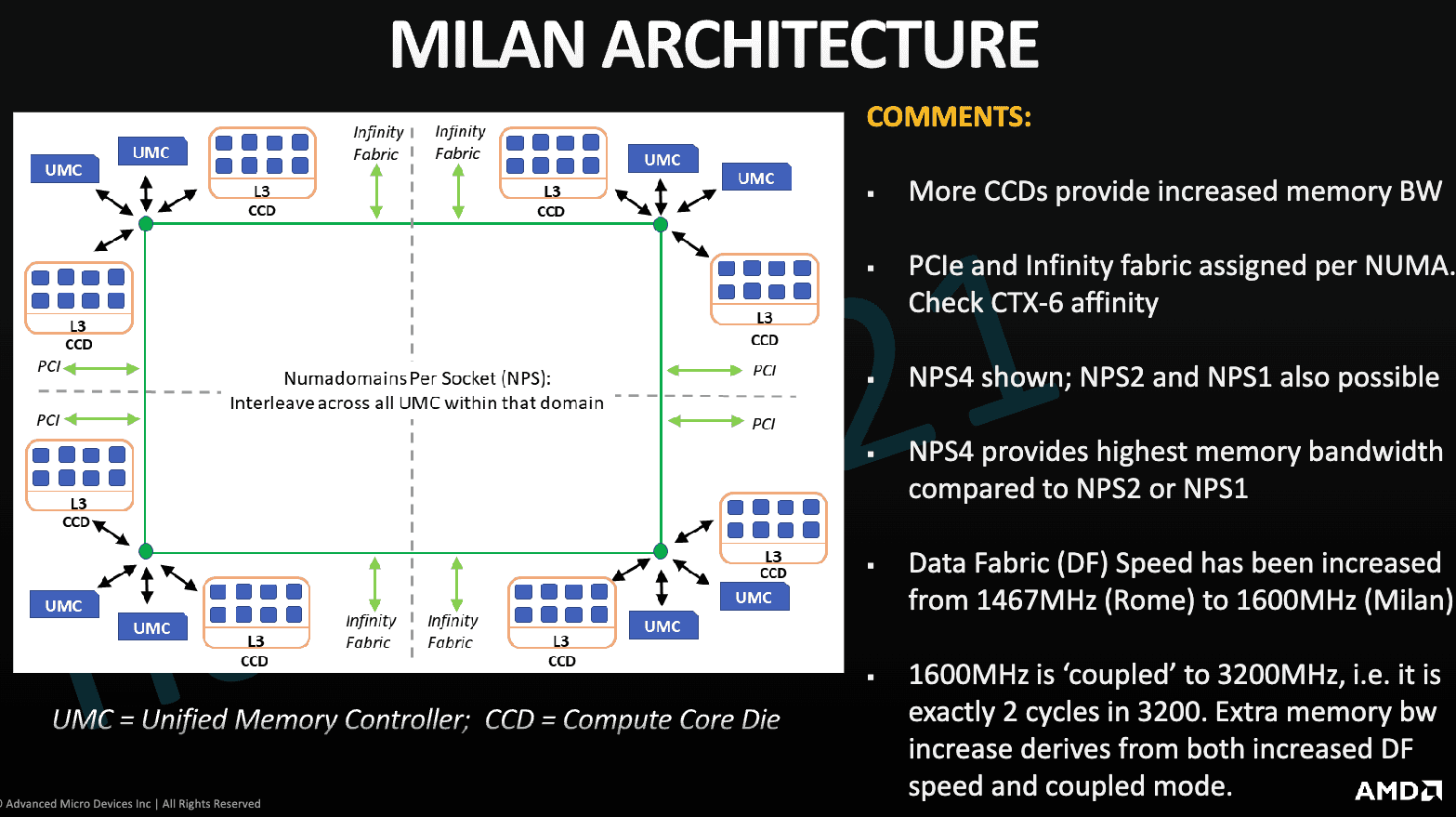
NPS 4
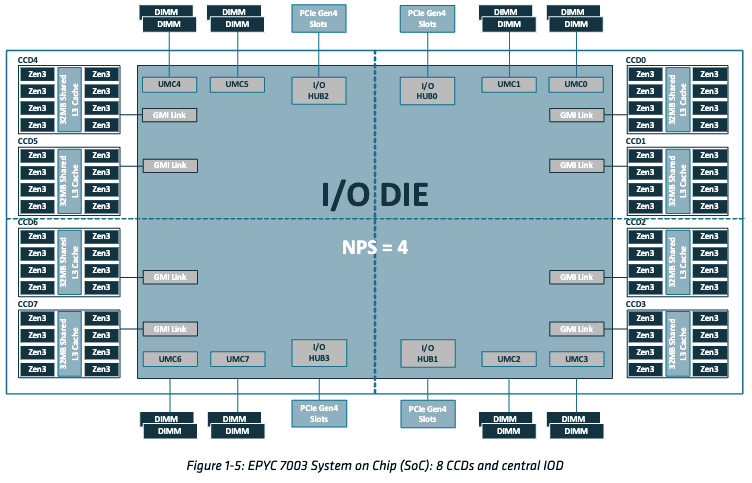
(source)
EPYC 7763 - 2 Socket
For two-socket system, the communication between EPYC 7763 is through 4 xGMI-2(Infinity Fabric Gen 2) links.
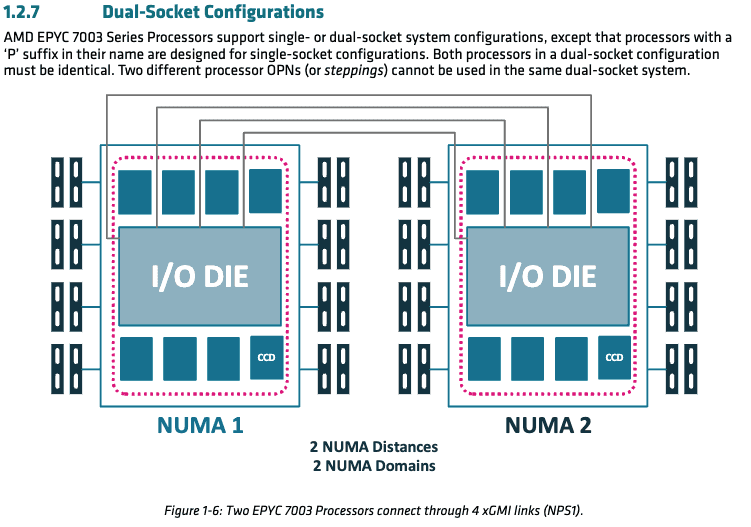 (source)
(source)
Review: AMD Epyc 7763 2P (Milan) - CPU - HEXUS.net - Page 2
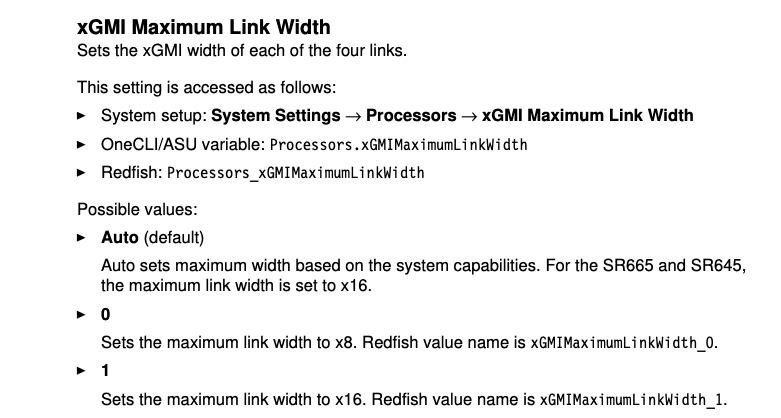
xGMI related
Cross socket interconnect for 7763
- 4-Link xGMI-2
- Max Speed : 18GT/s
- Maximum Link Width : x16
Theoretical maximum bandwidth for cross-socket communication. :
\(4 * 18GT/s * 16bits/transfer * (1/8) bytes/bit = 144 GB/s\)
\(144GB/s * 60\% = 86.4 GB/s\)
How to calculate ? refer to AMD Rome Processors - HECC Knowledge Base
For EPYC 7742
In each Rome node configured with the HPE Apollo 9000 system architecture, there are 3 xGMI links using a total of 48 PCIe lanes. With the xGMI link speed set at 16 GT/s, the theoretical throughput for each direction is 96 GB/s (3 links x 16 GT/s x 2 bytes/transfer) without factoring in the encoding for xGMI, since there is no publication from AMD available. However, the expected efficiencies are 66–75%, so the sustained bandwidth per direction will be 63.5–72 GB/s.
some references:
EPYC 7773x
The 7773x is similar to the 7763, except for the difference in L3 cache size.
96MB L3 cache per CCD. (32MB + 64MB 3D V-Cache)
AMD EPYC 7773X Specs | TechPowerUp CPU Database
AMD “Zen 3” 3D Vertical Cache Detailed Some More | TechPowerUp
Deep Diving Zen 3 V-Cache – Chips and Cheese
Some test result
AMD 7773x NPS2 mode
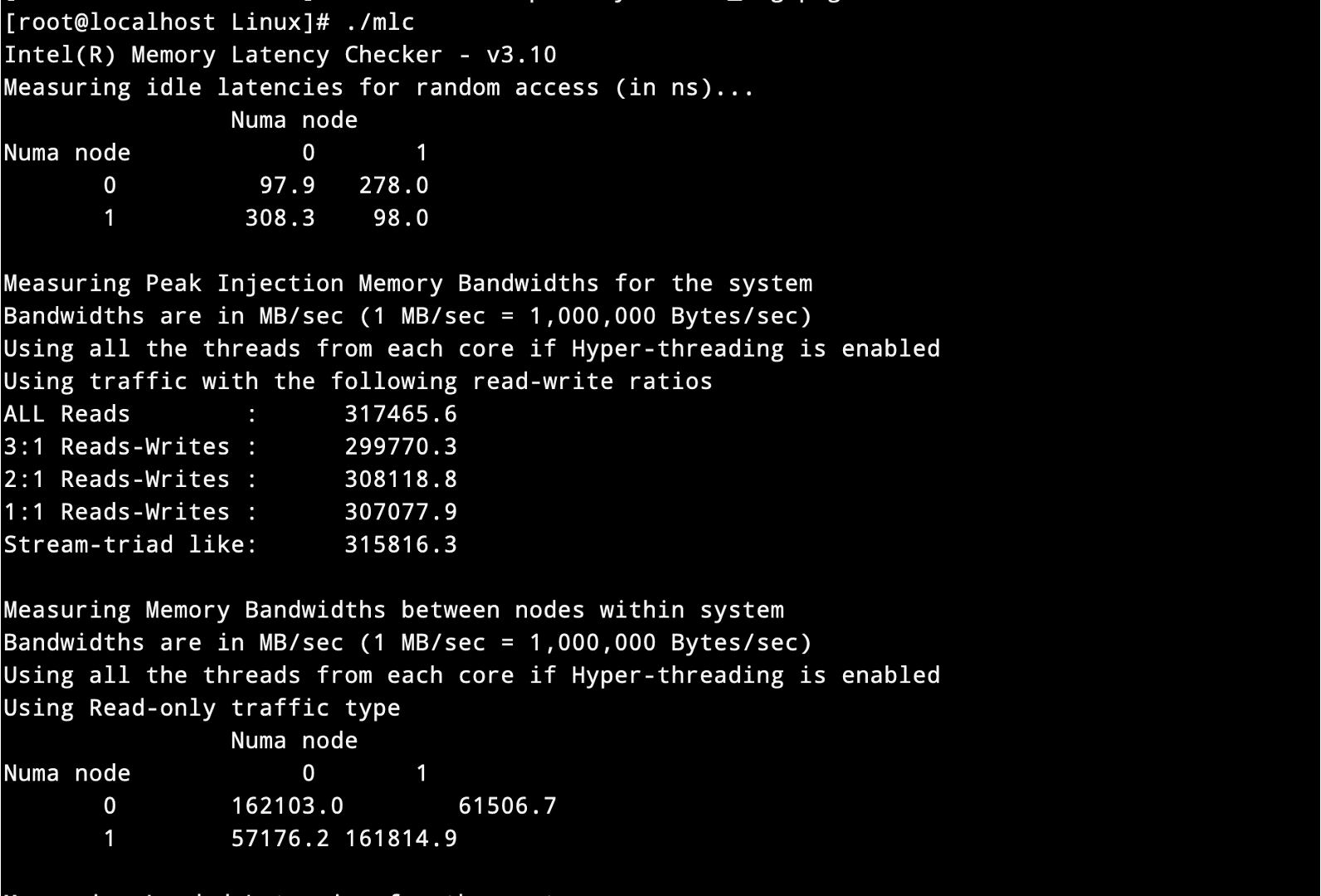
AMD 7773x NPS4 mode
$ cat nps4.log
Intel(R) Memory Latency Checker - v3.10
*** Unable to modify prefetchers (try executing 'modprobe msr')
*** So, enabling random access for latency measurements
Measuring idle latencies for random access (in ns)...
Numa node
Numa node 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 84.7 93.4 101.8 104.6 172.8 177.4 171.7 172.3
1 92.8 85.7 104.7 100.5 179.0 183.0 176.7 178.0
2 101.0 104.8 85.9 92.6 173.3 179.9 175.6 176.1
3 104.4 101.6 93.3 84.5 177.1 183.4 182.1 183.2
4 173.3 177.5 175.6 176.6 86.1 93.3 101.7 104.6
5 179.3 183.2 181.2 181.2 92.6 85.7 104.7 100.5
6 169.2 174.6 175.6 177.7 100.5 104.7 85.7 92.6
7 175.9 180.7 181.2 187.0 104.4 101.6 93.3 86.1
Measuring Peak Injection Memory Bandwidths for the system
Bandwidths are in MB/sec (1 MB/sec = 1,000,000 Bytes/sec)
Using all the threads from each core if Hyper-threading is enabled
Using traffic with the following read-write ratios
ALL Reads : 356352.3
3:1 Reads-Writes : 322368.2
2:1 Reads-Writes : 318636.4
1:1 Reads-Writes : 310333.6
Stream-triad like: 323440.8
Measuring Memory Bandwidths between nodes within system
Bandwidths are in MB/sec (1 MB/sec = 1,000,000 Bytes/sec)
Using all the threads from each core if Hyper-threading is enabled
Using Read-only traffic type
Numa node
Numa node 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 44538.4 44004.2 43184.1 42758.6 24522.6 23993.0 23872.8 24716.7
1 43988.9 44562.7 42721.3 43210.6 24560.3 34338.6 24718.8 24684.9
2 43160.7 42725.0 44546.2 44019.6 24520.7 24844.4 24690.3 23863.1
3 42704.5 43131.0 43962.0 44506.2 23519.0 23690.0 24464.4 24403.7
4 24397.7 24461.7 24317.2 23554.7 44582.6 43972.4 43163.3 42734.7
5 24680.3 34208.9 24887.2 24376.8 43964.5 44516.6 42696.0 43200.9
6 23491.7 23893.6 24539.3 24437.4 43211.4 42732.6 44517.6 43985.0
7 24575.8 23864.0 23453.3 24472.6 42720.5 43142.2 43930.1 44468.4
Measuring Loaded Latencies for the system
Using all the threads from each core if Hyper-threading is enabled
Using Read-only traffic type
Inject Latency Bandwidth
Delay (ns) MB/sec
==========================
00000 920.83 356069.6
00002 924.85 355460.4
00008 920.38 356391.8
00015 909.86 356797.4
00050 891.06 357606.7
00100 887.14 357646.8
00200 497.61 357489.2
00300 143.45 279058.4
00400 130.96 216713.9
00500 125.18 177043.2
00700 119.40 129561.3
01000 115.38 92492.1
01300 112.84 71951.3
01700 104.98 55619.7
02500 102.25 38317.6
03500 101.50 27687.9
05000 100.67 19648.4
09000 100.28 11244.0
20000 100.07 5425.4
Measuring cache-to-cache transfer latency (in ns)...
Local Socket L2->L2 HIT latency 23.8
Local Socket L2->L2 HITM latency 27.1
Remote Socket L2->L2 HITM latency (data address homed in writer socket)
Reader Numa Node
Writer Numa Node 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 - 107.1 113.6 117.4 185.3 191.5 181.2 187.9
1 106.4 - 117.7 113.7 189.2 195.4 185.1 191.7
2 114.0 117.4 - 106.2 186.9 193.1 186.6 193.2
3 117.6 113.7 106.2 - 186.7 193.5 190.7 197.3
4 185.9 192.3 186.5 190.7 - 106.8 114.3 118.7
5 189.1 195.4 189.7 193.8 106.9 - 117.5 114.4
6 182.4 188.8 186.7 194.6 114.5 117.5 - 106.9
7 185.3 191.6 189.5 197.4 118.8 114.3 106.9 -
Remote Socket L2->L2 HITM latency (data address homed in reader socket)
Reader Numa Node
Writer Numa Node 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0 - 107.5 116.9 121.8 188.9 197.8 184.2 194.0
1 107.6 - 122.0 116.8 194.0 202.8 189.3 199.0
2 117.1 121.8 - 107.4 189.8 201.1 190.1 199.8
3 122.0 116.7 107.4 - 190.8 202.8 195.5 205.2
4 189.5 197.8 190.6 196.7 - 108.0 117.4 123.1
5 193.8 202.2 194.9 201.0 108.1 - 121.9 117.4
6 185.3 193.7 190.3 201.3 117.6 121.9 - 108.0
7 189.5 197.9 194.4 205.4 123.2 117.5 108.0 -Reference
- EPYC 7763 - AMD - WikiChip
- AMD EPYC™ 7763 | AMD
- AMD EPYC 7763 Specs | TechPowerUp CPU Database
- high-performance-computing-tuning-guide-amd-epyc7003-series-processors.pdf
some reference data:
Notes mentioning this note
There are no notes linking to this note.